Nobel Laureates
Nobel Laureates
Over the course of our history, 45 members have been awarded a Nobel Prize in Physics, Chemistry or Physiology/Medicine.
Physics
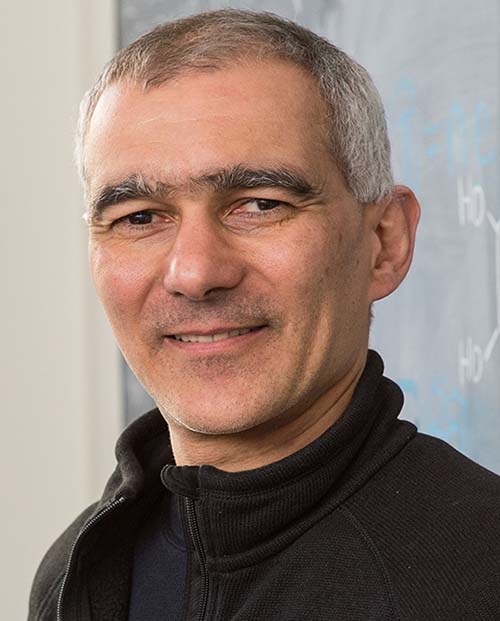
Pierre Agostini (2023)
Optica Fellow

(jointly with Frenec Krausz and Anne L’Huillier) “for experimental methods that generate attosecond pulses of light for the study of electron dynamics in matter.”
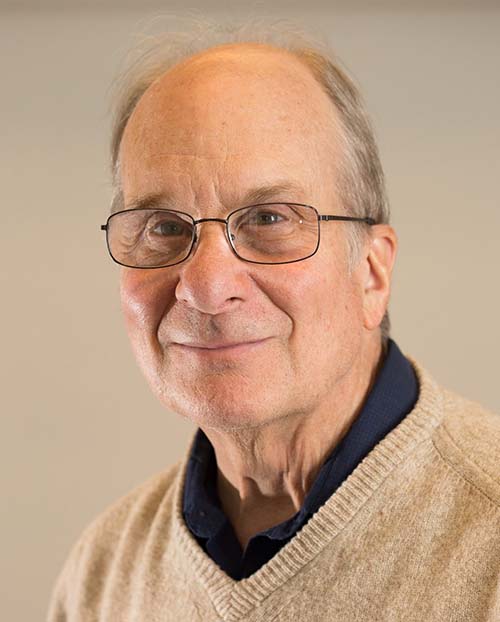
Ferenc Krausz (2023)
Optica Fellow

(jointly with Pierre Agostini and Anne L’Huillier) “for experimental methods that generate attosecond pulses of light for the study of electron dynamics in matter.”
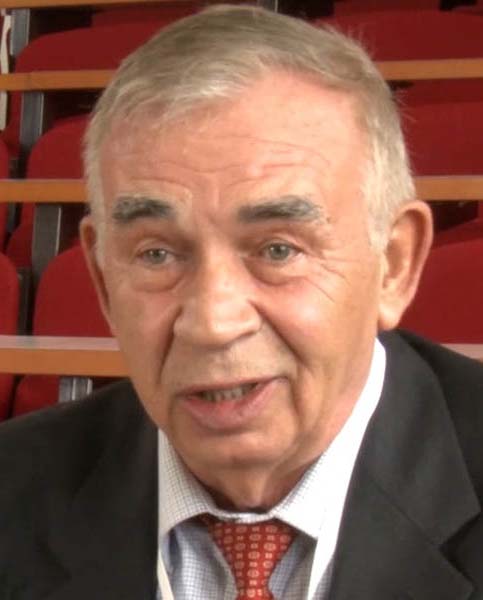
Anne L’Huillier (2023)
Optica Fellow
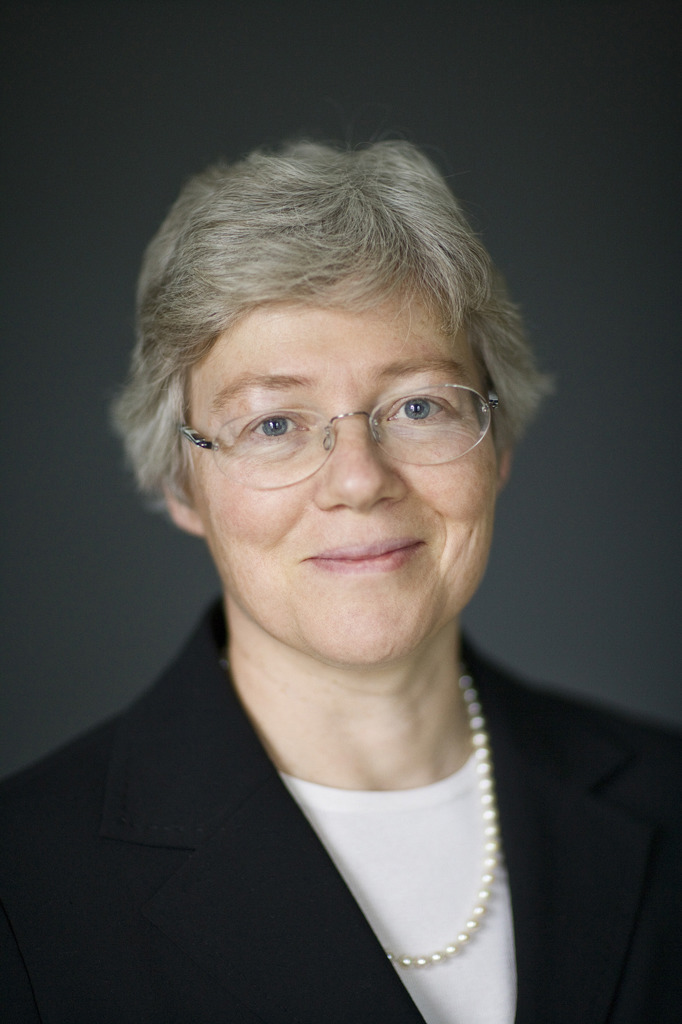

(jointly with Pierre Agostini and Ferenc Krausz) “for experimental methods that generate attosecond pulses of light for the study of electron dynamics in matter.”
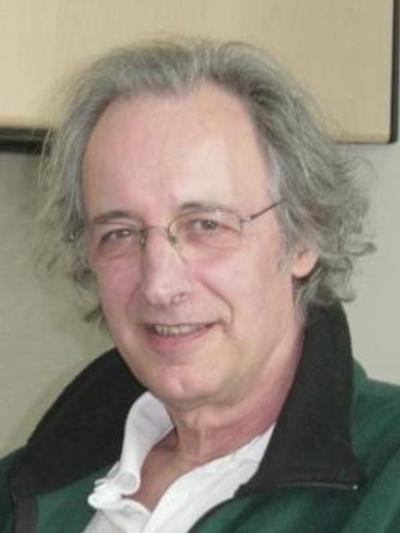
Alain Aspect (2022)
Optica Honorary Member

(jointly with John F. Clauser and Anton Zeilinger) "for experiments with entangled photons, establishing the violation of Bell inequalities and pioneering quantum information science"
John F. Clauser (2022)
Optica Emeritus

(jointly with Alain Aspect and Anton Zeilinger) "for experiments with entangled photons, establishing the violation of Bell inequalities and pioneering quantum information science"
Anton Zeilinger (2022)
Optica Fellow

(jointly with Alain Aspect and John F. Clauser) "for experiments with entangled photons, establishing the violation of Bell inequalities and pioneering quantum information science"
Arthur Ashkin (2018)
Optica Honorary Member

(one half of the prize) "the optical tweezers and their application to biological systems"
Gérard Mourou (2018)
Optica Fellow

(one half of the prize, jointly with Donna Strickland) "their method of generating high-intensity, ultra-short optical pulses"
Donna Strickland (2018)
Optica Honorary Member

(one half of the prize, jointly with Gérard Mourou) "their method of generating high-intensity, ultra-short optical pulses"
Barry C. Barish (2017)
 (jointly with Thorne and Weiss) "for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves."
(jointly with Thorne and Weiss) "for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves."
Kip S. Thorne (2017)
 (jointly with Barish and Weiss) "for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves."
(jointly with Barish and Weiss) "for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves."
Rainer Weiss (2017)

(jointly with Barish and Thorne) "for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves."
Isamu Akasaki (2014)

(jointly with Hiroshi Amano and Shuji Nakamura) "for the invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes which has enabled bright and energy-saving white light sources."
Hiroshi Amano (2014)
Optica Member

(jointly with Isamu Akasaki and Shuji Nakamura) "for the invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes which has enabled bright and energy-saving white light sources"
Shuji Nakamura (2014)

(jointly with Isamu Akasaki and Hiroshi Amano) "for the invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes which has enabled bright and energy-saving white light sources."
David J. Wineland (2012)
Optica Honorary Member
 "for ground-breaking experimental methods that enable measuring and manipulation of individual quantum systems"
"for ground-breaking experimental methods that enable measuring and manipulation of individual quantum systems"
Charles K. Kao (2009)
Optica Member

(one half of the prize) "for groundbreaking achievements concerning the transmission of light in fibers for optical communication"
Willard S. Boyle (2009)
Optica Member

(one half of the prize, jointly with George E. Smith) "for the invention of an imaging semiconductor circuit - the CCD sensor"
George E. Smith (2009)
Optica Member

(one half of the prize, jointly with Willard S. Boyle) "for the invention of an imaging semiconductor circuit - the CCD sensor"
John C. Mather (2006)
Optica Honorary Member

(jointly with George F. Smoot) "for their discovery of the blackbody form and anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background radiation"
George F. Smoot (2006)
Optica Honorary Member

(jointly with John C. Mather) "for their discovery of the blackbody form and anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background radiation"
Roy J. Glauber (2005)
Optica Honorary Member

(one half of the prize) "for his contribution to the quantum theory of optical coherence"
Theodor W. Haensch (2005)
Optica Honorary Member

(one half of the prize, jointly with John L. Hall) "for their contributions to the development of laser-based precision spectroscopy, including the optical frequency comb technique"
John L. Hall (2005)
Optica Honorary Member

(one half of the prize, jointly with Theodor W. Haensch) "for their contributions to the development of laser-based precision spectroscopy, including the optical frequency comb technique"
Eric Cornell (2001)
Optica Fellow

(jointly with Wolfgang Ketterle and Carl E. Wieman) "for the achievement of Bose-Einstein condensation in dilute gases of alkali atoms, and for early fundamental studies of the properties of the condensates"
Wolfgang Ketterle (2001)
Optica Fellow

(jointly with Eric A. Cornell and Carl E. Wieman) "for the achievement of Bose-Einstein condensation in dilute gases of alkali atoms, and for early fundamental studies of the properties of the condensates"
Carl Wieman (2001)
Optica Fellow

(jointly with Eric A. Cornell and Wolfgang Ketterle) "for the achievement of Bose-Einstein condensation in dilute gases of alkali atoms, and for early fundamental studies of the properties of the condensates"
Zhores I. Alferov (2000)
Optica Fellow

(one half of the prize, jointly with Herbert Kroemer) "for basic work on information and communication technology"
Herbert Kroemer (2000)

(one half of the prize, jointly with Zhores I. Alferov) "for developing semiconductor heterostructures used in high-speed- and opto-electronics."
Steven Chu (1997)
Optica Honorary Member

(jointly with Claude Cohen-Tannoudji and William D. Phillips) "for development of methods to cool and trap atoms with laser light"
Claude Cohen-Tannoudji (1997)
Optica Honorary Member

(jointly with Steven Chu and William D. Phillips) "for development of methods to cool and trap atoms with laser light"
William D. Phillips (1997)
Optica Honorary Member

(jointly with Steven Chu and Claude Cohen-Tannoudji) "for development of methods to cool and trap atoms with laser light"
Hans G. Dehmelt (1989)

(one half of the prize, jointly with Wolfgang Paul) "for the development of the ion trap technique.”
Wolfgang Paul (1989)

(one half of the prize, jointly with Hans G. Dehmelt) "for the development of the ion trap technique.”
Norman F. Ramsey (1989)
 (one half of the prize) "for the invention of the separated oscillatory fields method and its use in the hydrogen maser and other atomic clocks."
(one half of the prize) "for the invention of the separated oscillatory fields method and its use in the hydrogen maser and other atomic clocks."
Gerd Binnig (1986)

( one half of the prize, jointly with Heinrich Rohrer) "for their design of the scanning tunneling microscope.”
Heinrich Rohrer (1986)

( one half of the prize, jointly with Gerd Binnig) "for their design of the scanning tunneling microscope.”
Kai M. Siegbahn (1981)

(one half the prize) "for his contribution to the development of high-resolution electron spectroscopy."
Nicolaas Bloembergen (1981)
Optica Honorary Member

(one half of the prize, jointly with Arthur Leonard Schawlow) "for their contribution to the development of laser spectroscopy"
Arthur L. Schawlow (1981)
Optica Honorary Member

(one half of the prize, jointly with Nicolaas Bloembergen) "for their contribution to the development of laser spectroscopy"
Arno Penzias (1978)

(one half of the prize, jointly with Robert Woodrow Wilson) "for their discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation.”
Robert W. Wilson (1978)

(one half of the prize, jointly with Arno Allan Penzias) "for their discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation.”
James Rainwater (1975)
Optica Fellow

(jointly with Aage Niels Bohr and Ben Roy Mottelson) "for the discovery of the connection between collective motion and particle motion in atomic nuclei and the development of the theory of the structure of the atomic nucleus based on this connection"
Dennis Gabor (1971)
Optica Honorary Member
 "for his invention and development of the holographic method"
"for his invention and development of the holographic method"
Alfred Kastler (1966)
Optica Honorary Member
 "for the discovery and development of optical methods for studying Hertzian resonances in atoms"
"for the discovery and development of optical methods for studying Hertzian resonances in atoms"
Richard P. Feynman (1965)

(jointly with Sin-Itiro Tomonaga and Julian Schwinger) "for their fundamental work in quantum electrodynamics, with deep-ploughing consequences for the physics of elementary particles.”
Julian Schwinger (1965)

(jointly with Sin-Itiro Tomonaga and Richard P. Feynman) "for their fundamental work in quantum electrodynamics, with deep-ploughing consequences for the physics of elementary particles.”
Sin-Itiro Tomonaga (1965)

(jointly with Julian Schwinger and Richard P. Feynman) "for their fundamental work in quantum electrodynamics, with deep-ploughing consequences for the physics of elementary particles.”
Nicolay Gennadiyevich Basov (1964)

(one half of the prize, jointly with Aleksandr Mikhailovich Prokhorov) "for fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics, which has led to the construction of oscillators and amplifiers based on the maser-laser principle."
Aleksandr Mikhailovich Prokhorov (1964)
Optica Honorary Member

(one half of the prize, jointly with Nicolay Gennadiyevich Basov) "for fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics, which has led to the construction of oscillators and amplifiers based on the maser-laser principle"
Charles H. Townes (1964)
Optica Honorary Member

(one half of prize) "for fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics, which has led to the construction of oscillators and amplifiers based on the maser-laser principle"
Polykarp Kusch (1955)

(one half of the prize) "for his precision determination of the magnetic moment of the electron.”
Willis Eugene Lamb (1955)
Optica Honorary Member

(one half of the prize) "for his discoveries concerning the fine structure of the hydrogen spectrum"
Max Born (1954)

(one half of the prize) "for his fundamental research in quantum mechanics, especially for his statistical interpretation of the wavefunction."
Frederik Zernike (1953)
Optica Honorary Member
 "for his demonstration of the phase contrast method, especially for his invention of the phase contrast microscope"
"for his demonstration of the phase contrast method, especially for his invention of the phase contrast microscope"
Isidor Isaac Rabi (1944)
 "for his resonance method for recording the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei.”
"for his resonance method for recording the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei.”
Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac (1933)

(jointly with Erwin Schrödinger) "for the discovery of new productive forms of atomic theory."
Erwin Schrödinger (1933)

(jointly with Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac) "for the discovery of new productive forms of atomic theory."
Werner Heisenberg (1932)
 “for the creation of quantum mechanics, the application of which has, inter alia, led to the discovery of the allotropic forms of hydrogen.”
“for the creation of quantum mechanics, the application of which has, inter alia, led to the discovery of the allotropic forms of hydrogen.”
Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (1930)
Optica Honorary Member
 "for his work on the scattering of light and for the discovery of the effect named after him"
"for his work on the scattering of light and for the discovery of the effect named after him"
Robert Andrews Millikan (1923)
Optica Honorary Member
 "for his work on the elementary charge of electricity and on the photoelectric effect"
"for his work on the elementary charge of electricity and on the photoelectric effect"
Niels Bohr (1922)
 "for his services in the investigation of the structure of atoms and of the radiation emanating from them.”
"for his services in the investigation of the structure of atoms and of the radiation emanating from them.”
Albert Einstein (1921)
 "for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect.”
"for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect.”
Johannes Stark (1919)
 "for his discovery of the Doppler effect in canal rays and the splitting of spectral lines in electric fields.”
"for his discovery of the Doppler effect in canal rays and the splitting of spectral lines in electric fields.”
Max Planck (1918)
 "in recognition of the services he rendered to the advancement of Physics by his discovery of energy quanta."
"in recognition of the services he rendered to the advancement of Physics by his discovery of energy quanta."
Sir William Henry Bragg (1915)

(jointly with William Lawrence Bragg) “for their services in the analysis of crystal structure by means of X-rays."
Sir William Lawrence Bragg (1915)

(jointly with Sir William Henry Bragg) “for their services in the analysis of crystal structure by means of X-rays."
Max von Laue (1914)
 "for his discovery of the diffraction of X-rays by crystals.”
"for his discovery of the diffraction of X-rays by crystals.”
Guglielmo Marconi (1909)

(jointly with Karl Ferdinand Braun) "in recognition of their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy."
Karl Ferdinand Braun (1909)

(jointly with Guglielmo Marconi) "in recognition of their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy."
Gabriel Lippmann (1908)
 "for his method of reproducing colours photographically based on the phenomenon of interference.”
"for his method of reproducing colours photographically based on the phenomenon of interference.”
Albert Abraham Michelson (1907)
Optica Honorary Member
 "for his optical precision instruments and the spectroscopic and metrological investigations carried out with their aid"
"for his optical precision instruments and the spectroscopic and metrological investigations carried out with their aid"
Lord Rayleigh (John William Strutt) (1904)
 "for his investigations of the densities of the most important gases and for his discovery of argon in connection with these studies.”
"for his investigations of the densities of the most important gases and for his discovery of argon in connection with these studies.”
Hendrik Antoon Lorentz (1902)

(jointly with Pieter Zeeman) "in recognition of the extraordinary service they rendered by their researches into the influence of magnetism upon radiation phenomena."
Pieter Zeeman (1902)

(jointly with Hendrik Antoon Lorentz) "in recognition of the extraordinary service they rendered by their researches into the influence of magnetism upon radiation phenomena."
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen (1901)
 "in recognition of the extraordinary services he has rendered by the discovery of the remarkable rays subsequently named after him.”
"in recognition of the extraordinary services he has rendered by the discovery of the remarkable rays subsequently named after him.”
Chemistry
(jointly with Louis Brus and Alexei Ekimov) “for the discovery and synthesis of quantum dots.”
(jointly with Moungi Bawendi and Alexei Ekimov) “for the discovery and synthesis of quantum dots.”
(Jointly with Moungi Bawendi and Louis Brus) “for the discovery and synthesis of quantum dots.”
Jacques Dubochet (2017)

(jointly with Joachim Frank and Richard Henderson ) "for developing cryo-electron microscopy for the high-resolution structure determination of biomolecules in solution."
Joachim Frank (2017)

(jointly with Jacques Dubochet and Richard Henderson ) "for developing cryo-electron microscopy for the high-resolution structure determination of biomolecules in solution."
Richard Henderson (2017)

(jointly with Jacques Dubochet and Joachim Frank) "for developing cryo-electron microscopy for the high-resolution structure determination of biomolecules in solution."
(jointly with Stefan W. Hell and W. E. Moerner) "for the development of super-resolved fluorescence microscopy"
Stefan W. Hell (2014)
Optica Fellow

(jointly with Eric Betzig and W. E. Moerner) "for the development of super-resolved fluorescence microscopy"
W. E. Moerner (2014)
Optica Fellow

(jointly with Eric Betzig and Stefan W. Hell) "for the development of super-resolved fluorescence microscopy"
Martin Chalfie (2008)

(jointly with Osamu Shimomura and Roger Y. Tsien) "for the discovery and development of the green fluorescent protein, GFP.”
Osamu Shimomura (2008)

(jointly with Martin Chalfie and Roger Y. Tsien) "for the discovery and development of the green fluorescent protein, GFP."
Roger Y. Tsien (2008)

(jointly with Osamu Shimomura and Martin Chalfie) "for the discovery and development of the green fluorescent protein, GFP.”
Gerhard Ertl (2007)
 "for his studies of chemical processes on solid surfaces.”
"for his studies of chemical processes on solid surfaces.”
Koichi Tanaka (2002)

(jointly with John B. Fenn, one-half of the prize) "for their development of soft desorption ionisation methods for mass spectrometric analyses of biological macromolecules."
John B. Fenn (2002)

(jointly with Koichi Tanaka, one-half of the prize) "for their development of soft desorption ionisation methods for mass spectrometric analyses of biological macromolecules."
Ahmed H. Zewail (1999)
 "for his studies of the transition states of chemical reactions using femtosecond spectroscopy."
"for his studies of the transition states of chemical reactions using femtosecond spectroscopy."
Robert F. Curl, Jr. (1996)
Optica Fellow

"for their discovery of fullerenes"
Gerhard Herzberg (1971)
Optica Honorary Member
 "for his contributions to the knowledge of electronic structure and geometry of molecules, particularly free radicals"
"for his contributions to the knowledge of electronic structure and geometry of molecules, particularly free radicals"
Ronald George Wreyford Norrish (1967)

( one half of the prize, jointly with George Porter) "for their studies of extremely fast chemical reactions, effected by disturbing the equlibrium by means of very short pulses of energy.”
George Porter (1967)

(one half of the prize, jointly with Ronald George Wreyford Norrish) "for their studies of extremely fast chemical reactions, effected by disturbing the equlibrium by means of very short pulses of energy.”
Physiology/Medicine
Haldan Keffer Hartline (1967)
Optica Honorary Member

(jointly with Ragnar Granit and George Wald) "for their discoveries concerning the primary physiological and chemical visual processes in the eye"
George Wald (1967)
Optica Honorary Member

(jointly with Ragnar Granit and Haldan Keffer Hartline) "for their discoveries concerning the primary physiological and chemical visual processes in the eye"
Sir John Carew Eccles (1963)

(jointly with Alan Lloyd Hodgkin and Andrew Fielding Huxley) "for their discoveries concerning the ionic mechanisms involved in excitation and inhibition in the peripheral and central portions of the nerve cell membrane.”
Alan Lloyd Hodgkin (1963)

(jointly with Sir John Carew Eccles and Andrew Fielding Huxley) "for their discoveries concerning the ionic mechanisms involved in excitation and inhibition in the peripheral and central portions of the nerve cell membrane.”
Andrew Fielding Huxley (1963)

(jointly with Sir John Carew Eccles and Alan Lloyd Hodgkin) "for their discoveries concerning the ionic mechanisms involved in excitation and inhibition in the peripheral and central portions of the nerve cell membrane.”




