Sir David Payne on the Power of Light
Sir David Payne on the Power of Light
Rebecca B. Andersen
Accessible, Affordable Global Communications
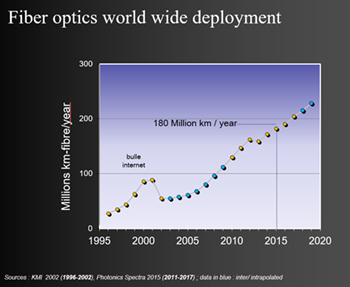 “By 2020, there will be 200+ millions of kilometers of fiber optic networks around the world,” said Payne. “It would take a single individual more than 5 million years to watch the amount of video that will be streamed across global IP networks at this time.”
“By 2020, there will be 200+ millions of kilometers of fiber optic networks around the world,” said Payne. “It would take a single individual more than 5 million years to watch the amount of video that will be streamed across global IP networks at this time.”In order to address a capacity crunch in next generation networks, Payne explained how hollow-core fibers will enable the next phase in fiber technology. The hollow-core microstructured optical fibers (HC MOFs) are a special kind of optical fibers which confine the light inside a hollow core surrounded by a microstructured cladding. The key advantage of HC MOFs is that the radiation propagates mostly in the air core and optical damage threshold is raised. Hollow core photonic crystal fibers (HC PCFs) can guide the light by virtue of a photonic band gap or due to an inhibited coupling between the air core modes and the cladding modes.
The secret to hollow-core fiber is doing away with the cladding and replacing it with photonic crystals. The light shoots down the hollow core, and when it strikes the edge, the photonic crystals bounce the photons. By doing away with the plastic/glass, these hollow-core fibers have lower signal loss (allowing for longer distances between repeaters), and the increased speed of light (about 30% faster than plastic/glass) reduces latency. This is a big opportunity, Payne notes, for “financial institutions looking for speed-of-light trading.”
Going Beyond the Network with Optical Fibers
 The ESO Very Large Telescope Interferometer (VLTI) today allows astronomers to see details up to 25 times finer than with individual telescopes. With one such telescope, images of celestial objects as faint as magnitude 30 can be obtained in a one-hour exposure. This corresponds to seeing objects that are four billion (four thousand million) times fainter than what can be seen with the unaided eye.
The ESO Very Large Telescope Interferometer (VLTI) today allows astronomers to see details up to 25 times finer than with individual telescopes. With one such telescope, images of celestial objects as faint as magnitude 30 can be obtained in a one-hour exposure. This corresponds to seeing objects that are four billion (four thousand million) times fainter than what can be seen with the unaided eye.Becoming popular in the early 1990’s with Japanese auto manufacturers, optical fiber gyroscopes have consumer and industrial applications in motion control, industrial processing and consumer electronics. More sensitive optical fiber gyroscopes have applications in inertial guidance systems, defense navigation and platform stabilization. The most advanced optical fiber gyroscopes can even detect minute changes in the rotational rate of the Earth.
 Payne concluded his presentation by sharing one of his proudest moments in his career. In early 2015, his team at the University of Southampton announced that they had discovered a way to store data in five dimensions on nanostructure glass that can survive for billions of years. They developed the write and read processes of five dimensional (5D) digital data through femtosecond laser writing, where they use short bursts of high intensity light to encode a quantum bit, (a qubit) through the polarization of a single photon. The self-assembled nanostructures in the glass (which is fused quartz) change the way light travels through it, modifying polarization of light. This technology was then used to preserve one of oldest documents in British history – the 800 year old Magna Carta.
Payne concluded his presentation by sharing one of his proudest moments in his career. In early 2015, his team at the University of Southampton announced that they had discovered a way to store data in five dimensions on nanostructure glass that can survive for billions of years. They developed the write and read processes of five dimensional (5D) digital data through femtosecond laser writing, where they use short bursts of high intensity light to encode a quantum bit, (a qubit) through the polarization of a single photon. The self-assembled nanostructures in the glass (which is fused quartz) change the way light travels through it, modifying polarization of light. This technology was then used to preserve one of oldest documents in British history – the 800 year old Magna Carta.Noting that “There are always visionaries who see the light!” – Payne looks to quantum technology, high energy physics, sensors, mid-IR, disruptive materials (2D), storage and the ‘Internet of Things’ which will continue to drive advancements in optical fibers.
About Professor Sir David N. Payne
Professor Sir David Neil Payne CBE FRS FREng is a leading Professor at the University of Southampton and Director of the Optoelectronics Research Centre. A world class pioneer of technology, his work has had a great impact on telecommunications and laser technology over the last forty years. The vast transmission capacity of today’s internet results directly from the erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) invented by David and his team in the 1980s. His pioneering work in fiber fabrication in the 70s resulted in almost all of the special fibers in use today including fiber lasers which are currently undergoing rapid growth for application in manufacturing and defense. David has made numerous leading contributions to many diverse fields of photonics and is widely acknowledged as an inventor of key components.
